The Internet of Things is getting everywhere—from lighting control in your yard to rocket engine factories. 94% of businesses will use IoT by the end of 2021, according to Microsoft’s IoT Signals report.
IoT is growing super-fast. Every day there are new, better IoT ideas because of new technologies like 5G, edge computing, or even digital twins.
What are the most promising IoT trends for now, which industries adopt IoT faster, and what to expect from smart sensors—in this guide.
Table of Contents
5 IoT Trends for 2020
First things first—let’s start with discussing IoT trends for 2020. Here are the most recent trends that’ll help you see the full picture of IoT and what it can bring to businesses.
#1. 5G and IoT
You know that 5G is fast, but how fast exactly? It’s download-an-HD-movie-in-seconds fast. But it’s not just speed when it comes to IoT.
5G allows us to control a broader range of devices via mobile apps—from a smart kettle to heavy machinery and public transport.
5G offers lower latency (delay time) and broad coverage, which makes the idea of autonomous vehicles closer to reality. Smart cars, trucks, and buses can move without delays due to 5G in a smooth flow of traffic.

But that’s not just it. Companies that already work with IoT expect 5G to boost their IoT revenue streams through private network opportunities and manufacturing environment support. As well as through robotics, autonomous vehicles, and technologies like AR/VR.
#2. Global Connectivity
Сonnectivity may seem simple, but in reality communication between sensors and devices is a complicated part of the network. Especially when these devices should work across a range of countries.
Still, there’s an ever-rising demand for IoT connectivity—national, regional, or global—in many fields. From car manufacturing or pump connectivity to IoT in healthcare.
Here’s an example of IoT connectivity in the healthcare sector. Brighter, a Swedish health tech company, realized there might be the demand for a connected insulin dispenser. They created Actiste, a pocket-sized connected device that measures glucose levels and makes injections.
They faced a problem, though: how do you make Actiste work with a range of networks in a range of countries? Brighter found a way out by choosing an out-of-the-box connectivity solution from a European provider.
That’s just one example. The number of such connectivity solutions and providers will only grow as grows the need for global connectivity.
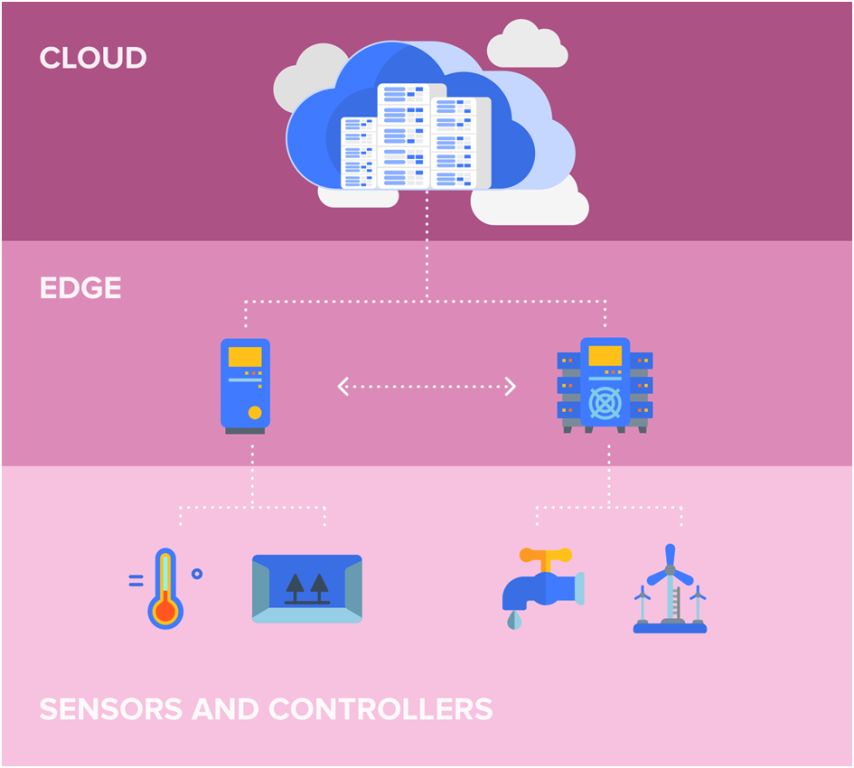
#3. Edge Computing
One internet-connected camera that monitors your warehouse and sends real-time data to an office isn’t a big deal.
Now, what if there are hundreds of such cameras sending live video at the same time? The video quality will be much lower, while bandwidth will cost pretty much.
IoT devices, 5G fast wireless, real-time data processing, and analytics need a lot of computing power. That’s why edge computing makes perfect sense.
What’s edge computing exactly? Basically, it’s a technology that brings computation and data storage closer to the devices that gather it, not a central database that can be hundreds of miles away.
This way, there wouldn’t be any delays with data—especially real-time data—transmitting which often makes apps run slower.
Edge-computing software/hardware handles this by processing and storing data locally. An IoT sensor, a tablet or laptop, or the security camera I’ve mentioned—they all can be edge devices.
#4. IoT-AR Solutions
Both AR and IoT have huge potential. While IoT fills a gap between physical-digital infrastructure, AR overlays digital information on top of the physical environment. That’s an impressive symbiosis.
IoT+AR combination changes how people interact with the world around them. IoT-AR solutions help visualize, analyze, understand data, and make smarter decisions based on the information.
For example, IoT+AR can increase the speed of picking orders on warehouses. DHL is already using sensors throughout their warehouses, while head-mounted AR devices guide workers to the product’s location. This way, employees take the shortest routes, pick good faster, and work more productively.
#5. Digital Twins and IIoT
Basically, a digital twin is a replica of a real device or an object. With a digital twin, as the name indicates, you have two versions of an object: the physical one and the digital twin one.
In real life, digital twins are mainly used in the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)—engineering and manufacturing. Anything can be a twin— a hydraulic pump or a jet engine.
For example, digital twins can simulate how equipment has performed over time. The more highly instrumented the equipment is, the more accurately digital twins might replicate their work with the help of IoT sensors.
That could help workers predict performance issues or breakdowns and their consequences.
Among digital twins solutions providers are:
- Microsoft Azure IoT
- General Electric
- Siemens
- IBM
What Industries Take Advantages of IoT, and How?
Here are four industries that can (and do) take advantage of IoT.
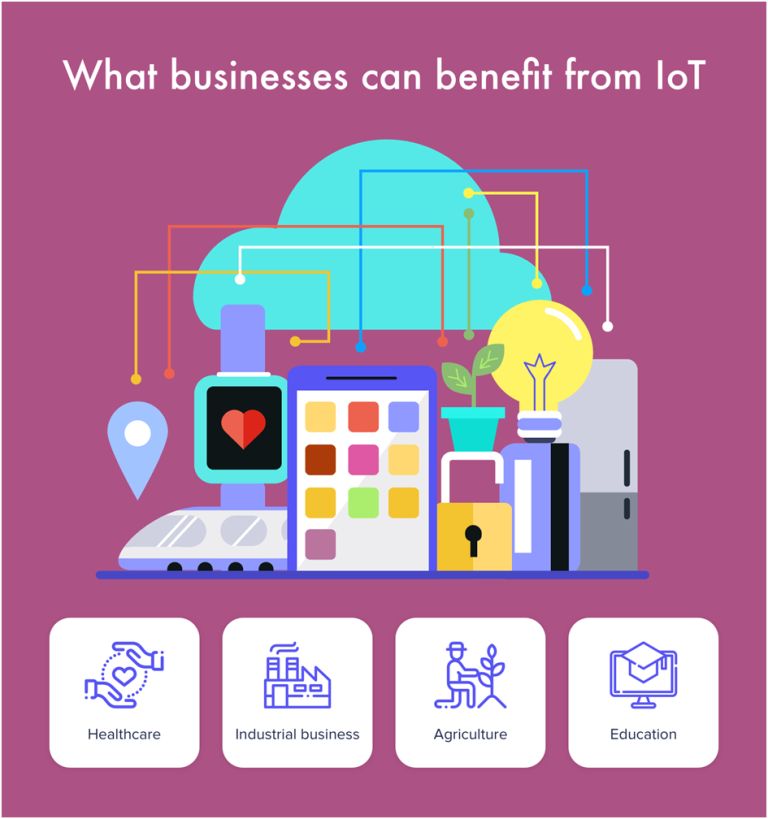
Healthcare
The most popular IoT solution in medicine is wearables—partially because of the ever-rising popularity of healthcare app development.
Wearables and mobile devices let medical workers monitor patients’ condition remotely, without visiting them (very handy during COVID-19 pandemic).
By using devices like fitness trackers, smartwatches, smart scales, and mobile devices, doctors get updates about stats of their patients—heart rate, weight, sleeping habits without checking on them personally.
And if case any indicators are too high or too low, doctors get in touch with their patients, warn them and give instructions.
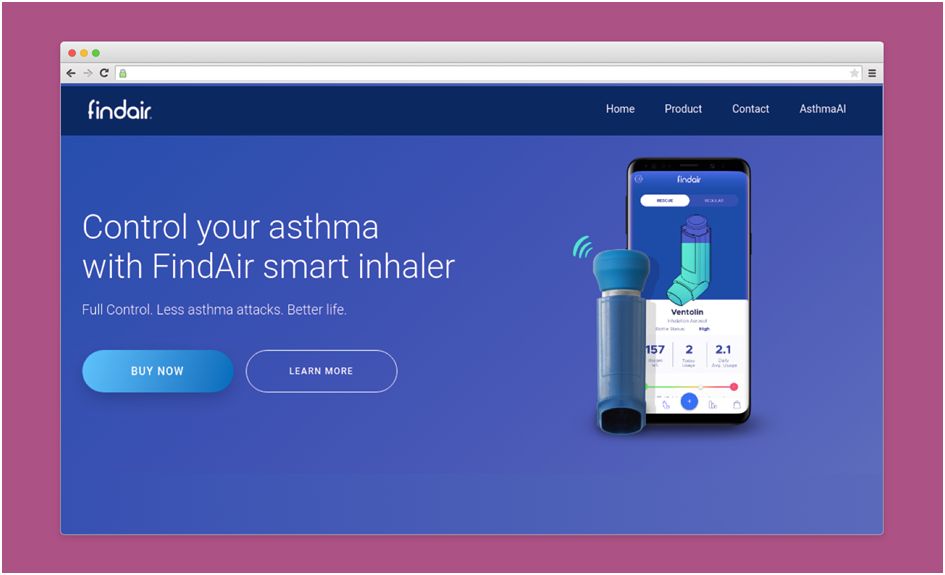
A good example here is a smart inhaler like FindAir that prevents asthma attacks. It has an in-built GPS module, and when a patient with asthma leaves the device in the house or at the office, FindAir sends a push notification to their smartphone.
Besides, FindAir is capable of analyzing the environment and predicting factors that cause the attack.
Agriculture
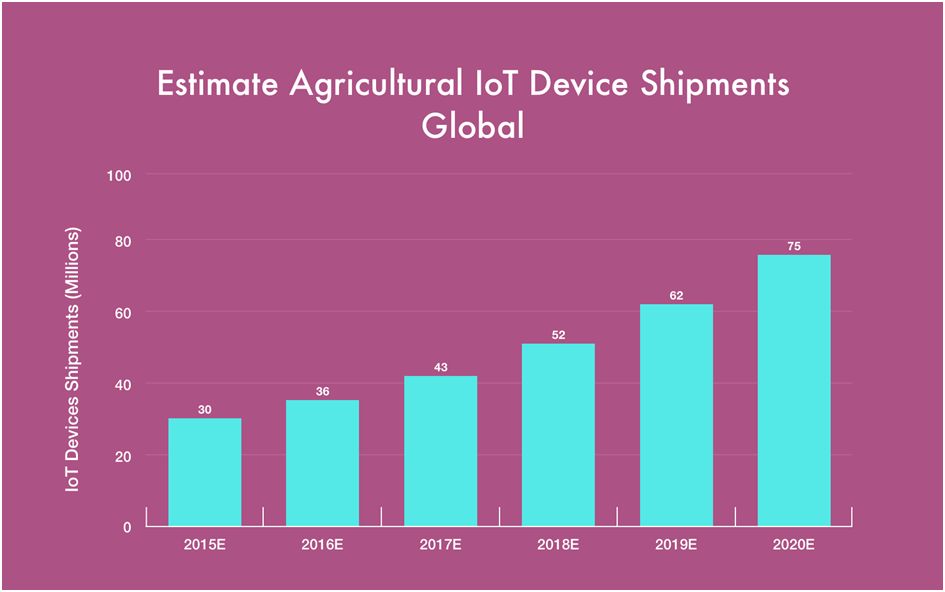
IoT-powered agriculture is becoming more commonplace (not as fast as it deserves, though). Back in 2018, the IoT farming market was worth $7.53B, and by 2023 it’s going to reach $13B.
Smart agriculture changes centuries-old methods of farming with technologies and IoT devices. Special sensors help farmers track almost everything on their land—from water level to cattle and weather conditions.
Here’s a couple of IoT-powered farming devices.
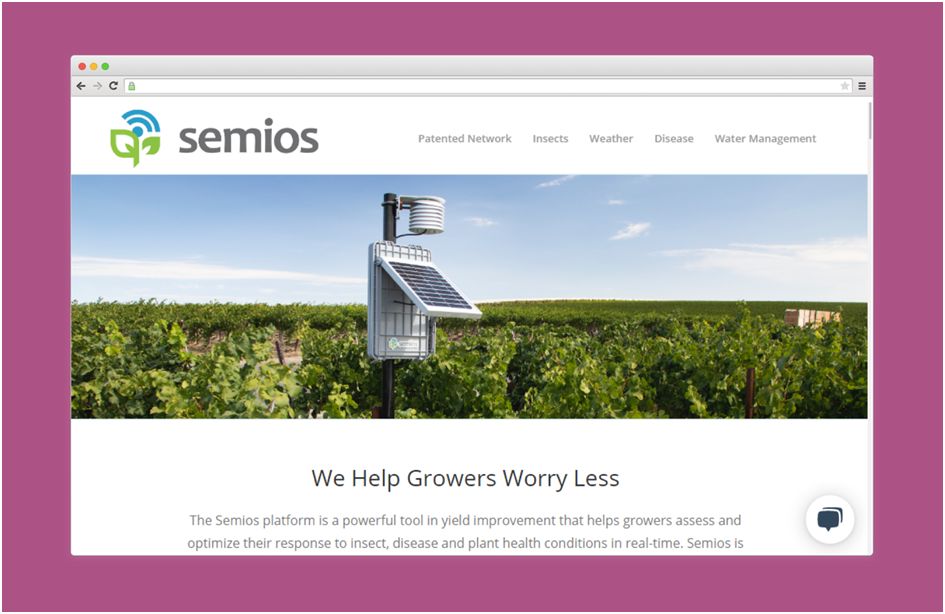
Semios, a platform that helps farmers worry less about their orchard or vineyard. The device uses a network of sensors to track and send reports in real-time, which helps farmers to optimize irrigation and keep control of pests.
Now, farmers aren’t just growing crops. They also breed animals who breathe, run, get stuck and sick, and being able to monitor their health and location is crucial to many farmers.
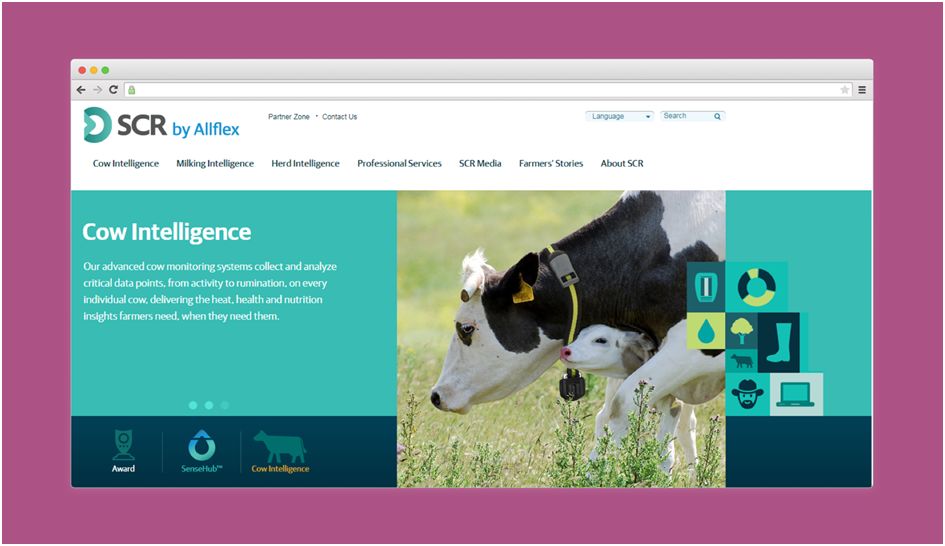
Cowlar, a smart non-invasive neck collar, monitors cow’s temperature, activity, and behavior. Farmers can get alerts and recommendations via text messages or calls made by a robot.
Education
When it comes to education, IoT helps both students, teachers, and even safeguards.
Let’s start with security matters.
Security is everything when it comes to children. But a single or even a couple of safeguards can’t protect the whole facility in a critical situation.
That’s why lots of IoT creators make IP cameras, motion sensors, and biometrics scanners—to keep edu establishments and those who work or study there safe.
But it’s not just about safety: IoT does a lot for students’ convenience and education boosting.
Geofencing is a great example here—with the help of beacons and a custom map, teachers can guide students through a building, be it a museum or an Art Gallery. Then the students will get pop-up notifications with interesting facts about the exhibits children are viewing.
A couple of more examples:
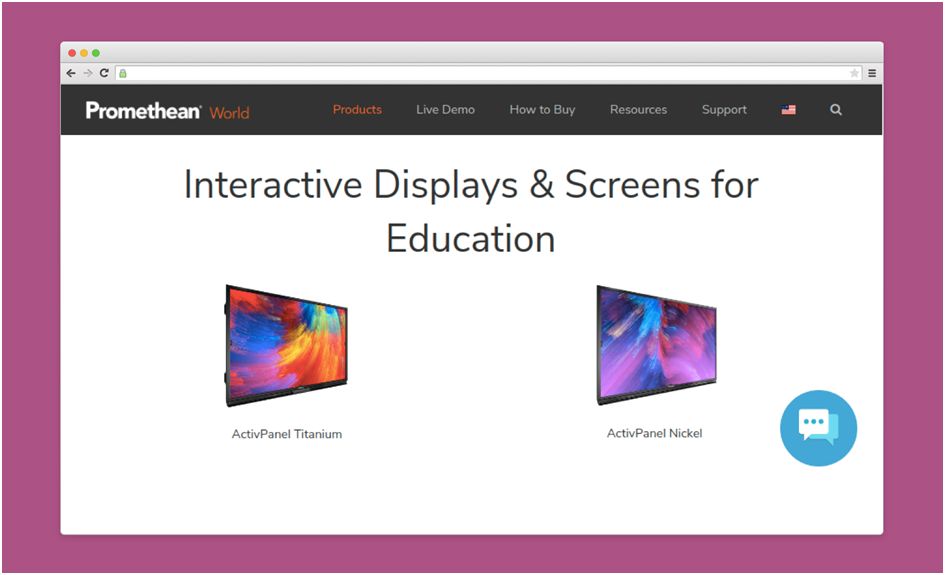
Promethean makes interactive displays for students. They combine multi-touch and natural writing technology, plus cloud-based lesson software and personalized training for teachers.
This way, students can better interact with academic material.
LocoRobo, a provider of programming and robotics education, uses robots to teach programming languages like Javascript, Python, C, or MATLAB. They even have LocoIoT course that explains how to design, build, and connect IoT systems.
Industrial Business
The bigger the plant is, the more machinery it uses. And the more time workers need to maintain its broken pieces.
IoT devices can be applied to a range of heavy equipment—to track quality, monitor its condition, and gather data.
Machine Vision, an Indonesian product, lets managers monitor the overall efficiency of their equipment. It uses sensors to give detailed statistics on the cause of any issues with the machinery.
Another case is quality monitoring. Mainly, workers see a defect only after the item’s ready and have to produce another one. Smart Solutions Industry product lets workers monitor the machine outcome in real-time and correct it if needed. With this feature, they may fix the issue in seconds and get a good-quality product in the end.
Let’s face it: IoT changes the way we live, work, and study. The latest IoT trends only show that there are no signs of stopping. IoT is growing fast with technologies like AR, 5G, edge computing, and other tech trends.
All that gives us a chance to work more effectively and have more control over everyday processes—from our smart houses to schools, offices, and workplaces.
Vitaly Kuprenko is a writer for Cleveroad. It’s a web and mobile app development company with headquarters in Ukraine. He enjoys writing about technology and digital marketing.